How Smart Cities Improve Sustainability and Efficiency
By Joe Braga
September 19, 2023
By Joe Braga
September 19, 2023
The perennial issue with sustainability initiatives in smart cities has always been economic viability. Citizens, companies and governments want to make greener choices and adopt more environmentally friendly habits. However, cost is a significant barrier.
Thanks to ongoing advances in IoT, smart cities can save money while being more energy-efficient and sustainable.
From waste bins to streetlights, smart cities are deploying a host of IoT-enabled solutions to:
Below are five of the primary areas where smart cities are improving environmental sustainability and energy efficiency.
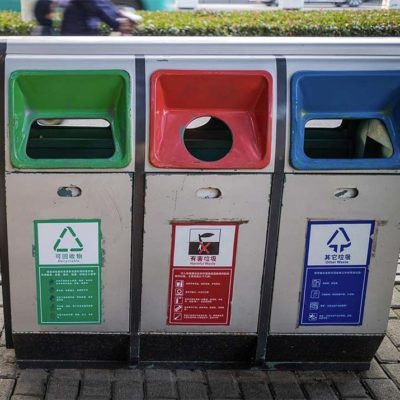

The U.S. produces 268 million tons of waste per year. Due to the nature of cities, waste accumulation can cause serious health problems and environmental damage. Unfortunately, the waste management industry uses outdated methods and processes.
Nevertheless, smart waste management solutions use IoT sensors to increase waste bin visibility. This enablement allows cities to monitor waste levels, which reduces unnecessary collection visits and vehicle emissions. It also prevents theft and overflow, which maintains quality sanitation. Moreover, the real-time data and insights from waste monitoring optimize pick-up scheduling and resource allocation.
As a side note, waste differentiation can be enhanced with various home appliances for waste management. These provide extensive analytics on consumer waste behavior and further simplify waste treatment at the door.
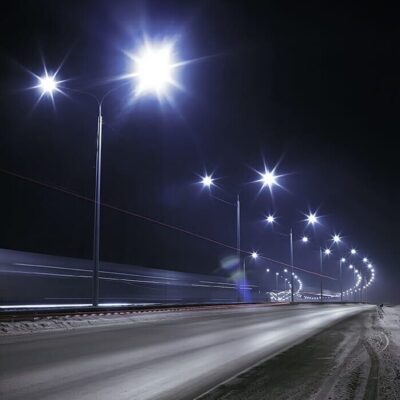

Street lighting, including public and commercial lighting, can become more energy efficient with IoT sensors. Smart street lighting systems help cities:
Smart lighting systems can also be integrated with solar panels. This integration can:
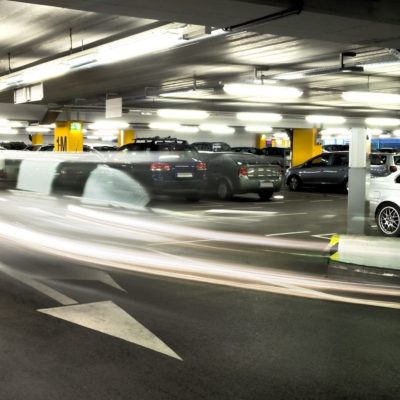

Smart cities can decrease emissions by leveraging smart traffic solutions, including:
These smart city technologies will trigger traffic alerts and allow traffic lights to adjust to assuage congestion. This capability can reduce the number of vehicles idling and degrading the air quality.
In addition, smart cities can install EV charging stations equipped with cellular IoT modules and SIMs for connectivity. EV charging stations can make alternative modes of transportation, such as electric vehicles and e-scooters, more feasible and sustainable.
Municipalities can work with main stakeholders to provide a well-distributed network of EV charging points. These charging points work with other smart city applications like smart traffic and public safety monitoring.

A home air conditioner can use around 3,000 watts of electricity in an hour — or 72,000 watts daily. Smart buildings and homes can help decrease these numbers.
IoT technology installed throughout a building’s appliances and systems (e.g., lighting and HVAC) permits automation and energy optimization efforts. For example, IoT devices can turn off lights and air conditioning to save energy if a home or office is empty. This ability can bring the building toward net-zero emissions.
Enhancing public safety and preventing crime is another key factor of smart buildings. Cameras, sound sensors and AI can be used to detect suspicious activities. This allows for a quick response to alert police or private security.

With IoT enablement for smart metering, water, gas and electricity utilities gain real-time data and insights to:
Smart metering is an essential enabler of smart grids. These grids empower utilities to improve efficiency and decrease operating costs. In addition, smart grids can more seamlessly incorporate sustainable energy sources. These would eliminate greenhouse gas emissions and enhance the reliability and resilience of the power system.
The key to a successful smart city program is synergy among the various projects, applications and services. You don’t have to trade economic viability for sustainability. Contact our IoT experts to learn how our IoT modules, connectivity plans and services, solutions and platforms can aid your smart city deployment.