Building the Smart Grid: IoT Energy Management Systems
August 12, 2025
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes

The Internet of Things (IoT) has reshaped how cities are conceptualized and planned. Cities worldwide now integrate digital technologies into their core systems. IoT devices connect people and governments to smart city solutions. These connections enable real-time data collection and analysis that supports city operations.
The ability to connect and control devices has given rise to smart grid technology. Modernized networks replace older network infrastructure with digital communications to increase efficiency. IoT supports cities as they become more adaptive and responsive to the needs of their governments and residents.

A “smart grid” is a digitally managed electricity network in which software and IoT sensors manage power flow. With smart grids, utilities manage supply and demand, monitor the grid for service problems and respond proactively to issues.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the smart grid is critical to building a secure, clean future. It is a mission-critical asset of an IoT framework. It can be used to monitor and remotely manage:
As smart city initiatives continue to proliferate worldwide, smart grids play an integral role in their success. Aging power grids can’t withstand the immense draw on resources and the need to transmit data for billions of consumers worldwide. Adopting smart grid technology can help municipalities and utilities:
Smart grids connect through private, dedicated networks and link devices distributed to businesses and homes citywide, including:
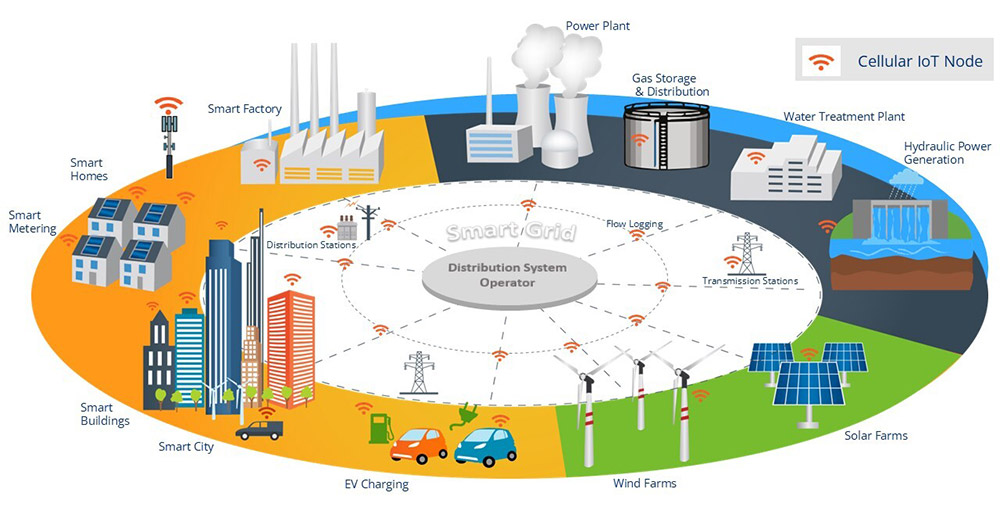
Smart grid IoT technologies contribute to robust and efficient energy management solutions lacking in the current framework. IoT smart grids provide two-way communication between connected devices and hardware that senses and responds to user demands. As a result, a smart grid is more responsive and less costly than the current power infrastructure.
Rapid, large-scale worldwide deployments of renewable energy architecture continue to reshape the grid. The rise in infrastructure installations — like wind farms and solar panels — disrupts the integration of disparate energy sources.
Artificial intelligence (AI) can help. It is playing an increasing role in smart grid management.
AI and machine learning models analyze real-time data from IoT sensors and regulate power to optimize the load. If a grid has a surplus of electricity — from solar panels, for example — an AI system can redirect it to needed locations. Those areas receive an improved balance of supply and demand.
AI-powered software also monitors grid status and maintenance and can respond automatically. In the case of a wildfire or other emergency, it can trigger a power shutoff.

Smart grid technologies help reduce energy consumption and costs via usage and data maintenance. Intelligent lighting through smart city technology can:
For consumer applications, users can adjust the temperature of their home thermostats through apps while at work or on vacation.

Smart grid technologies put less demand on batteries and are more carbon efficient. They are designed to reduce the peak load on distribution feeders. The U.S. Department of Energy is integrating green technology into its IoT smart management for more sustainable solutions. These solutions have the potential to benefit all distribution chains and include:

The 2025 Report Card for America’s Infrastructure states, “advancement[s] in smart grid technologies can improve operational efficiency and reduce the risks of outage events.” Through the use of smart grids, utility operators can proactively manage potential issues.
The report also details AI’s emerging role in smart grid operations. AI can:
As the world’s population grows, older grids won’t keep up with increased demand. Smart grids reduce outages through smart energy IoT monitoring and source rerouting for rapid recovery during a power failure.
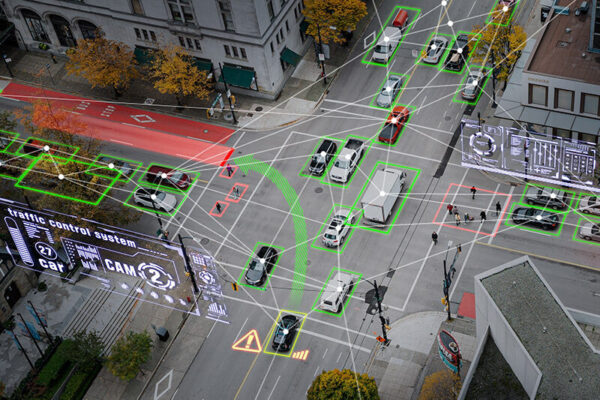
IoT smart sensors collect real-time data from electric vehicles and relay information to drivers and authorities. Accessing this data from smart sensors will enable cities to:
A 2024 International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies article explains how smart grids help manage energy consumption and reduce carbon emissions in rural areas.
IoT sensors combined with AI-powered tools and software optimize power system development and integrate with larger nearby grids. These grids will be critical for deploying new power infrastructures in developing countries facing population overflow.
Starting with the latest technology ensures the best path to economic growth.
Optimized smart city solutions provide greater insight into regional issues. Imagine a smart grid in a dry area set up to respond to a regional drought or wildfires. Adaptive city fog lighting would benefit a city in the northeast U.S. but would be ineffective elsewhere.
Customized technology and better data collection can improve the lives of regional populations.

Cybersecurity vulnerabilities elicit concern as smart city and smart utility infrastructure roll out worldwide. In the U.S., the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is creating a strategy to manage cybersecurity risks. NIST will also issue recommended standards for smart infrastructure, such as IoT modules.
At Telit Cinterion, we’re committed to IoT cybersecurity. Our modules and services enable secure communication and data encryption for smart grid and smart city devices and solutions.
Contact us to learn how our IoT modules, connectivity plans and services and solutions help cities worldwide improve:
Editor’s note: This blog was originally published on 10 May 2018 and has since been updated.