Cellular in SD-WAN: Why It Matters
By Safi Khan
January 7, 2021
The cloud, big data, analytics, mobility, Internet of Things (IoT) and social collaboration are just some of the technologies unlocking unprecedented innovation and transforming every business operation aspect. However, for CIOs, this new development can be more of a headache than a blessing.
Enterprises have long relied only on private networks to give their subsidiaries, branches or stores secure, highly available and high-performing access to applications and business management systems residing within their private data centers. However, the enterprise network’s capacity is in higher demand as data requirements increase due to the rising use of videos, guest networks, IoT data, and time- and latency-sensitive applications, such as voice and secure transactions. Traffic intended for the cloud is now taking an out-of-the-way route to its destination.
Unfortunately, this new reality is only increasing operational costs, penalizing quality of service (QoS) and performance, and consuming not easily upgradeable enterprise network capacity. This is driving the desire for two investments:
While it would be easy to resist deploying a cloud platform or any other high-connectivity technology, businesses cannot afford to sacrifice the potential of these investments. Could 5G cellular SD-WAN be the missing link to seizing the benefits of today’s latest technology while maintaining the control, reliability, visibility and security that enterprises value most?
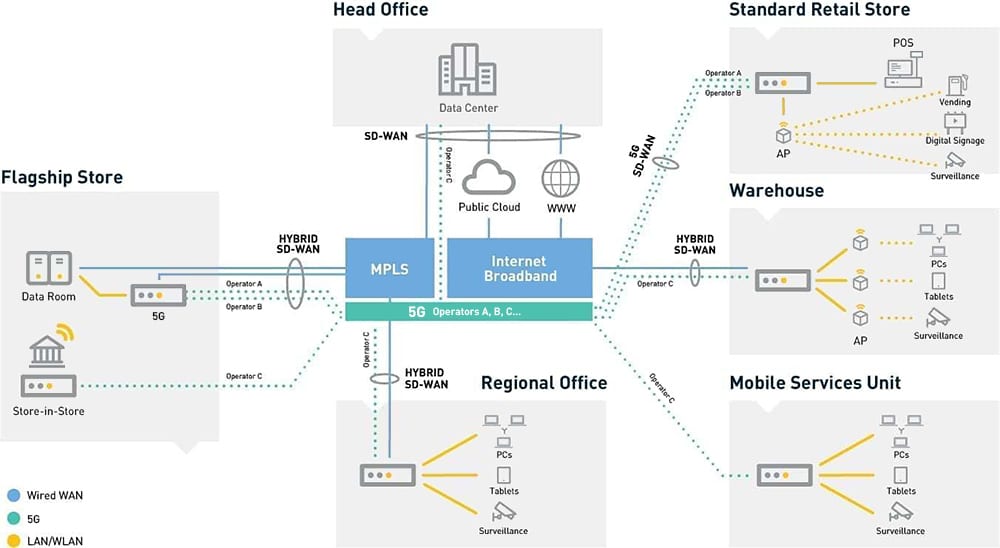
Software-defined wide-area networks (SD-WANs) promise to revolutionize how businesses connect with their distributed chain of physical locations. It simplifies and accelerates enterprise connectivity by combining multiple branch links with intelligent traffic directing across those links and policy-driven WAN management.
SD-WAN enables businesses to take advantage of three fundamental capabilities:
Businesses can dramatically lower the cost of their private WAN services and reduce outages, whether SD-WAN is deployed over public internet, LTE, 5G links, cloud-based private networks or 5G with a mix of MPLS, public internet and LTE. More importantly, employees and partners in remote locations gain the transparent, collaborative and knowledge-rich environment they need to succeed.
Wireless networks have evolved dramatically with LTE and now 5G. Operators worldwide have been upgrading so rapidly that traffic demand exploded with the increasing consumer appetite for social media and data-intensive applications. LTE-Advanced technologies and 5G wireless networks can offer peak data rates in the multi-gigabit per second (Gbps), which is well beyond the data rates provided by traditional public wired internet options short of fiber. With 3GPP Release (Rel) 16 rolling out in another year, 5G will usher in a new era, overlaying ultra-reliable and low-latency performance to current super-high data rates.
With the aggressive rollout of 5G, wireless technology has outpaced wired to the point that enterprises are finding it difficult to ignore. Early enterprise use cases for wireless include LTE failover. However, with ubiquitous coverage, increased network throughputs, including a dramatic increase in uplink throughputs compared to 4G, and one-millisecond latency, 5G has the power to become the primary connection for distributed enterprises.
Start by identifying a portfolio of high-speed, industrial-grade data cards available in NGFF M.2 and mini PCIe (mPCIe) form factors to support designs for mobile computing, networking and IoT applications. Look for plug-and-play integration simplicity covering the speed and performance you need and certifications for use in the countries and mobile operators you want. See below how Telit organizes its portfolio of data cards:
If your SD-WAN requires positioning or precision real-time clock performance, all the above data cards support global navigation satellite systems such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and Beidou.
These Telit data cards can help your business overcome the complexity, high costs and bandwidth limitations, maximizing the use of today’s LTE networks adaptively across regions and MNOs. For you, this means real-time, high-quality data exchange across cable, DSL, fiber, 4G and 5G with policy-based routing to application-specific traffic.
No more latency, no more limited connectivity and no more lost data — just direct internet access with connectivity guaranteed with a service level agreement and a seamless extension to cloud data centers and mobile devices.
Editor’s Note: This blog was originally published on 19 March 2018 and has since been updated.