Benefits of Smart Building Automation with IoT
By Bill Dykas
May 22, 2025
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes

Reducing operating costs and improving efficiency is a priority for more than building managers and real estate investors. Business owners and operators can cut energy and maintenance costs using Internet of Things (IoT) systems management platforms to turn their properties into smart buildings.
Operations that impact the bottom line can be improved by automating processes related to:
At the consumer level, smart homes leverage IoT devices and platforms to control devices, which will enable residents to:

A smart building or home is a structure with automated functions based on owner or manager specifications. IoT-connected technologies can now automate and simplify time-consuming tasks, which can be:
In addition to IoT, edge artificial intelligence (AI) and private networks are at the heart of building automation.
Smart building applications are getting smarter with microcontroller-based edge AI. Edge AI refers to the shift of artificial intelligence to devices at the network’s edge. These devices include sensors and IoT systems. Moving AI to the edge enables local data processing.
After accelerating AI in the cloud, AI came to the edge — specifically through microcontroller-based edge AI. This allows a range of use cases such as:
Edge AI consumes significantly less power and requires less runtime than a regular microcontroller. In addition to making machines more intelligent, edge AI allows for local decisions and faster responses. Smart building applications that use edge AI can still react to environmental changes even if communications are down.
The second trend driving building automation is 5G standardization, which allows companies to deploy dedicated cellular resources (i.e., private networks). For smart buildings, especially larger ones, unreliable connectivity options complicate device and resource management. A dedicated private cellular network ensures secure, flexible connectivity.
Various smart building trends are gaining traction. Property owners turn to IoT, AI and private networks to automate and secure many of their properties’ everyday functions. Smart homes and buildings can boost efficiency and provide cost savings through:

Optimizing the lighting and HVAC in your home or building can reduce your electric bill. Heating and cooling account for the highest annual electricity consumption in the U.S. residential sector. They are a major expense in commercial buildings.
Building automation systems (BAS) combine hardware and software to automate system management, such as HVAC and lighting, in one platform. Individual smart building upgrades, like connecting thermostats to apps for remote control and monitoring, will yield some energy savings. BAS’s integrated approach will maximize them.
The BAS is installed in new construction or as part of a retrofit in commercial buildings. Connecting disparate and legacy equipment might seem daunting. However, adding IoT sensors and a management platform to existing systems can be simpler and less costly than expected. Many providers design their products and platforms with retrofits in mind.
Home automation may involve a more piecemeal approach, with different apps to control HVAC and lighting systems. Some companies adopt the integrated BAS model for operating systems that connect and manage all residential technologies.

Edge AI and IoT-enabled cameras enhance the occupant experience. They can automatically adjust heating and lighting when people enter a room.
Integrated systems can also use AI-powered controls to monitor occupancy and optimize HVAC settings for greater efficiency. Multiple studies have found that thermal comfort in commercial environments influences productivity by approximately 8%.
A prime example of occupancy management technology is the Vision AppKit. This smart camera combines Telit Cinterion’s Wi-Fi and Bluetooth® wireless technology or LTE-M communication modules with Alif Semiconductor’s Ensemble E3 series MCU. The ultracompact Vision AppKit can perform on-device AI use cases — like face and object detection and image classification — at a lower power consumption.
Heating and cooling specific rooms at certain times will decrease the costs of providing optimal thermal comfort. An AI-powered occupancy management system can even detect when a building is unoccupied and shut it down, like turning off a computer.
Air quality and adequate ventilation have become major concerns in recent years. BAS can improve air quality and minimize the spread of pathogens, which can enhance occupant well-being and productivity. IoT air quality sensors in smart buildings can detect rising carbon monoxide levels and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) faster than humans.
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), VOCs include gases emitted from chemicals that have short- and long-term adverse health effects. VOC levels are up to 10 times higher indoors than outdoors. Good ventilation and air filtration can reduce this exposure. IoT sensors and AI tools can detect and fix threats before a property, or its occupants are at risk.
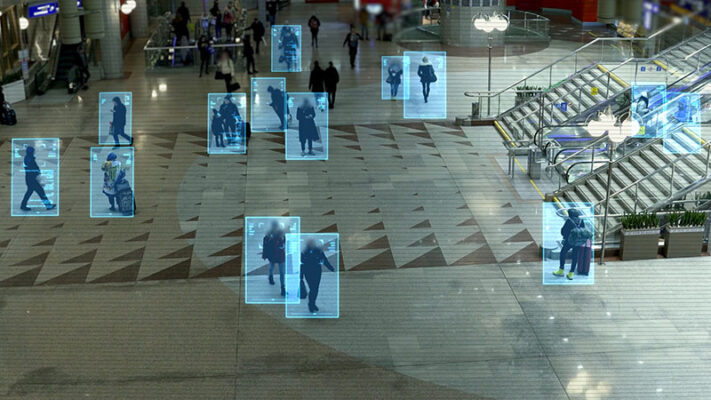

Connected physical security systems are rising as more businesses and homeowners adopt IoT technology. Connected security systems can provide a massive boost to safety and security in any building. These systems include:
The Vision AppKit enhances building security by improving person detection. This provides homeowners peace of mind even when they’re away.
Cybersecurity is another focus for smart building and smart home automation. More connected systems and devices create an expanded attack surface, leaving smart buildings and homes vulnerable to cyberattacks. A proactive cybersecurity approach can help businesses and residents keep their systems and devices safe.
Choose systems and providers that prioritize built-in security from the start. In addition, you can leverage private networks to:
Connecting sanitation devices with sensors helps smart buildings save water. IoT sensors installed in restrooms can monitor usage and create reports. The generated data helps facilities managers make informed decisions and note trends, like temperature control and water usage.
Connected edge-AI utility meters monitor water usage in smart homes and notify homeowners of unusual patterns. This monitoring can catch and control water leaks or other plumbing issues. Smart appliances can also support predictive maintenance. They self-detect mechanical problems to minimize the likelihood of costly repairs or replacements in the future.
Installing smart building and smart home IoT devices can lower homeowner premiums. Many insurance companies — having recognized the benefits of this technology — offer reduced rates for customers who use them. Some home insurers offer discounts of up to 20% for installing smart home devices or a home automation system.

Depending on the insurance company, you may find discounts for using:
Such systems can provide valuable data for insurance companies as they process claims. Suppose a homeowner reports a break-in. A video security system can provide data to help the insurance company sort out details and verify the damage.
IoT technologies can quickly detect potentially serious issues in a building (e.g., a gas leak or frozen pipe). They minimize damage and reduce insurance claims.
With Telit Cinterion, you can increase your organization’s real estate intelligence. Our 5G modules and data cards, IoT security solutions and deviceWISE® AI enhance your visibility and control over elements that impact your investment and bottom line.
Speak with our IoT experts to get started on your smart building application and propel your business to success. Contact Telit Cinterion
Editor’s note: This blog was originally published on 5 February 2018 and has since been updated.