A Guide to Best Security Practices for Smart Meters
By Neil Bosworth
April 4, 2024
By Neil Bosworth
April 4, 2024

The data generated from smart meters allow utilities and smart grid managers to improve service and efficiencies by:
Nevertheless, like any connected technology, smart meters are at risk of hackers exploiting them. In addition to accessing private consumption data and manipulating readings, cybercriminals can override individual meters and bring down entire grids.
Here are some guidelines for manufacturers to find the best partner and ensure product security.
Attack vectors are numerous. Smart meter manufacturers are responsible for securing their products and complying with evolving regulations.
Smart meter manufacturers must analyze supply chain processes to ensure the device is secure and doesn’t expose data. Manufacturers must also know who can manage connectivity configuration. This includes knowing who can activate or deactivate a device’s SIM card.
Figure 1 below shows additional areas smart meter manufacturers must consider, including corresponding security questions for IoT applications.
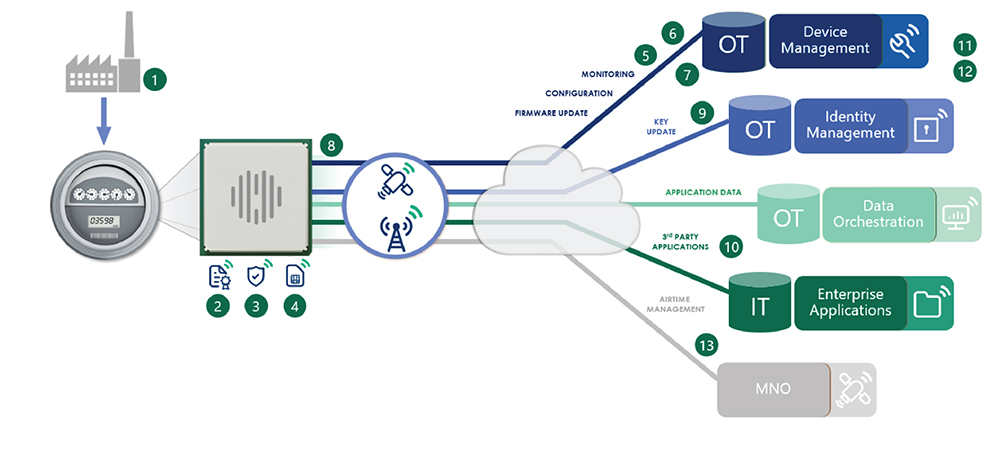
1. Has the device been compromised in manufacturing?
2. Can you trust the code running on the device?
3. Who can access and inspect the device?
4. Where is confidential information stored?
5. Can you update the firmware security patches?
6. Who can tamper with device settings?
7. Can you monitor device behavior?
8. Can you detect if your device is under attack?
9. Who manages digital identities and credentials?
10. Are the correct authentication and authorization layers for customer data access implemented?
11. Is the platform operated according to best practices and standards?
12. Where is the cloud platform hosted?
13. Who can manage or disable your SIM card?
It is also critical that smart meter manufacturers make their products interoperable. All smart meters will communicate with a head end system via a smart metering protocol called Device Language Message Specification (DLMS). DLMS plays a role in the wider security scheme. In addition, utilities must ensure that the data generated from smart meters within their domain is secure.

Smart meter deployments can last anywhere from 10 to 15 years. This point is frequently overlooked yet essential to realize when securing smart meters. Smart meter manufacturers must partner with a module and service supplier committed to life cycle support and security. Finding such a partner is crucial, especially considering evolving threats and emerging regulations.
An experienced supplier understands its systems aren’t stagnant solutions. This provider will safeguard the product software throughout its lifetime.
Module manufacturers must maintain their modules throughout the smart meter’s lifetime. They can do this by delivering firmware updates that address performance, stability and network configuration. In addition, these updates should address security to protect the meter from cyberthreats.
Smart meter manufacturers should prioritize those modules that are secure by design. Fixing security issues after deployment is difficult if security is not a major part of the module’s software.

The cybersecurity landscape is evolving, with hackers becoming more sophisticated year after year. To keep pace with hackers, regulators continue to roll out new standards.
As advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) evolves, smart meters are being forced to become complex communication devices to complement more sophisticated metrology. The metering industry is heavily regulated. However, the European Commission has introduced new blanket initiatives to tackle cybersecurity in internet-connected radio devices.
The industry is navigating the complexities of mapping existing harmonized standards to the Radio Equipment Directive Delegated Regulation (RED-DR) requirements. In addition, it’s preparing for the upcoming Cyber Resilience Act that will address IoT devices and systems.
ESMIG, the European association of smart energy solution providers, plays a key role in representing the meter industry. It addresses regulatory barriers to accelerate practical and realizable green energy transition.
As an active member, Telit Cinterion works with the industry by representing and demonstrating secure, interoperable communications. This is a fundamental requirement for successful metering deployments.
Telit Cinterion has been making smart meters smarter and enabling the evolution from automatic meter reading (AMR) to AMI. We’ve been a trusted partner for many organizations, successfully connecting millions of meters worldwide over the last 23 years.
Speak with our smart energy experts to discover how our comprehensive solutions can empower your IoT project.