The Role of IoT in Sustainable Farming Technology
By Martino Turcato
July 31, 2023
By Martino Turcato
July 31, 2023
If the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization’s projections are correct, 9.7 billion people will populate the earth in 2050. To support the global population, the organization says global food yields must increase 70% by then, with 90% of that growth happening on farmland already in use.
The agriculture industry faces extreme weather events and challenges like:
With production demands rising and resources becoming more limited, traditional farming practices are no longer up to the task.

There are myriad variables and conditions to monitor across a farm. Traditional farmers lose valuable time by:
They need to digitize and automate processes to achieve better visibility, efficiency and higher yields.
The solution is collecting data — and using IoT devices and applications to inform farming operations in real time.
IoT technology provides connectivity for precision agriculture, in which sensors collect data during all farm production phases. Precision agriculture uses variable rate technology (VRT) to increase efficiency and reduce waste. Crop inputs (e.g., seed, water, fertilizer and pesticide) are then optimized so that only the needed amounts are used in each area of the field. In addition, farmers can utilize connected sensors to monitor animal health and equipment maintenance needs.
IoT applications for sustainable farming systems include:
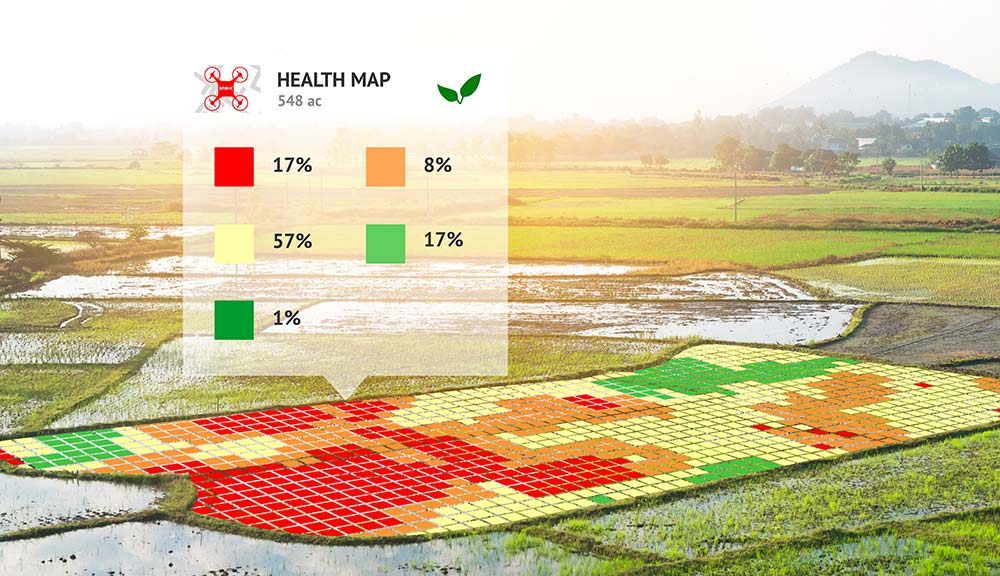
Sensors on harvesting machines collect data when they harvest crops and provide real-time moisture content measurements and other crop yield data. The system also allows operators to identify the more or less fertile parts of the field and change the number of seeds planted in those areas.
In sustainable farming, measuring soil moisture is critical for increasing irrigation system efficiency in areas with water scarcity and usage restrictions. Sensors collect information about soil moisture and send this data to remote systems that optimize irrigation pumping systems.
AI systems automatically analyze drone and satellite images of crops to detect signs of insect and other pest infestations. Specific solutions like traps can be monitored as well.
Many of these precision farming applications map out the fields and inputs. Therefore, they require accurate positioning.
GNSS receivers take advantage of global positioning systems. In addition, precise point positioning and real-time kinematic (PPP-RTK) technology achieve precision down to a few centimeters. These capabilities permit even multiple autonomous machines to coordinate with each other and avoid overlapping when plowing, sowing or harvesting.
Newer vehicles are equipped with devices and tools that send real-time diagnostic data to the cloud for analysis. This data helps with preventive maintenance and enables remote vehicle efficiency and location monitoring.
IoT data collection also enables blockchain applications. They ensure that secure, traceable data follows food products along the entire supply chain — from harvest to the point of sale.
Some farms still use short-range Wi-Fi and Bluetooth® wireless technology or unlicensed spectrum in the field. However, cellular low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) devices that use cellular technologies like LTE-M and NB-IoT are ideal for deployment in remote areas and other scenarios can provide better performance and deployment flexibility.
Furthermore, cellular LPWAN devices provide better coverage and can run on battery and direct power. These features make them ideal for many sustainable IoT agriculture use cases.
We offer the industry’s broadest portfolio of cellular LPWAN modules with best-in-class security and Power Saving Mode (PSM) and extended Discontinuous Reception (eDRX). We can also build your ready-to-launch sustainable smart agriculture solutions with our modules, connectivity and platforms.
Speak to our IoT agriculture experts to get started on your sustainable farming solution.