Embedded Connectivity: The Next Evolution in IoT
By Eyal Yasmin
January 9, 2025
Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
Embedded connectivity is when device manufacturers build connectivity into the device during manufacturing. It can refer to a module with a SIM embedded inside it.

Unlike the current market configuration in which the module and SIM are separated, embedded connectivity offers advantages, including:
A module with an embedded SIM acts as a smart engine. It combines module and SIM capabilities to provide a more productive and cost-effective way to use connectivity.

The current market solution (the first phase of connected module as a service) is typically offered as a bundle. The module and SIM come in the same package but are separated. In other words, the SIM is not embedded inside the module.
This first phase uses the embedded SIM (eSIM) machine-to-machine (M2M) technical specification SGP.02. It is sponsored by the Global System for Mobile Communications Association (GSMA).
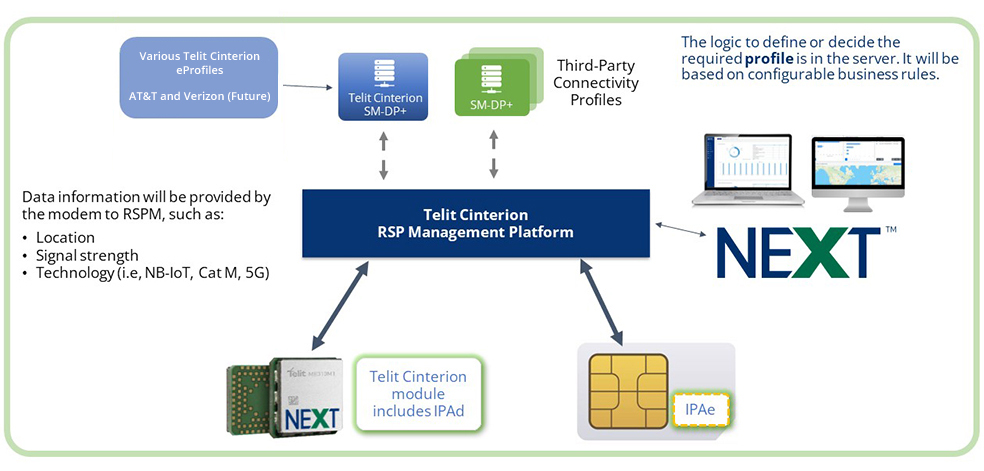
While the first phase of connected module as a service has benefits, the second phase is a significant enhancement of the GSMA SGP.22 specification. Placing the SIM inside the module eliminates the need to physically remove the SIM when replacing the existing profile or adding additional profiles.
The second phase also supports dynamic profile selection or the ability to select the most optimal profile, depending on the use case. Furthermore, it permits users to download profiles based on future needs without stressing about downloading the right profile on day one.
RSP depends on the embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card (eUICC), which uses the GSMA SGP.22 specification. The second phase will eventually use eSIM Internet of Things (IoT) technical specification SGP.32.
The embedded module is already supported in a specific module. More modules will be released at the end of 2024, enabling the second phase of connected module as a service. In addition, integrated SIM (iSIM) represents the next phase of embedded module connectivity and will be released in 2025.
Embedding the SIM inside the module has many technical advantages. For example, eSIMs offer:

Some leading solution providers will offer a module with a profile already inside it, commonly called bootstrapping. They will give the best profile for the particular use case, considering factors like the country the device will be deployed in and the requisite connectivity (e.g., Cat M, NB-IoT, 4G or 5G). This module will also have additional profiles already downloaded but not enabled. It automatically allows the module to select a second profile or any other as needed.
The benefits of a module with a full profile are manifold. If someone needed to deploy the module in a different location and didn’t want to use the default profile because of the country’s regulations, they could activate another profile. For example, in Brazil, regulations prevent roaming, so one would need to switch to a local profile. One could also enable the other backup profile to save money or to improve coverage.

Telit Cinterion is the module vendor and the SIM connectivity provider. We provide an end-to-end solution via our embedded connectivity portfolio, which leverages next-generation eSIM and iSIM technology.
Our embedded connectivity portfolio enables you to use our NExT™ profiles to deploy your cellular-connected IoT devices globally and out of the box. You can also expand with iSIM in accordance with global carrier plans. Moreover, our eUICC management tools support RSP management, saving you time and resources while boosting operational efficiency.
Speak with our IoT connectivity experts to simplify and future-proof your next cellular IoT device deployment.